A Deep Dive into the World of Apostille: Unveiling the Essentials
In an increasingly globalized environment, the necessity for a streamlined process to authenticate documents for international use has become paramount. Apostille, a term that resonates with legality, international affairs, and bureaucratic processes, serves as a cornerstone in the realm of document authentication. This article delves into the intricate world of apostilles, exploring their significance, the procedural nuances, and their pivotal role in international legal affairs.
The Genesis and Evolution of Apostille
The apostille system was birthed from the Hague Convention of 1961, which was established to abolish the requirement of legalization for foreign public documents. This convention laid the groundwork for a simplified method of certifying documents, making them recognized and accepted across signatory countries. The apostille, therefore, is a form of certification that is internationally acknowledged, ensuring that documents issued in one signatory country will be recognized as valid in another.

Understanding the Apostille Process
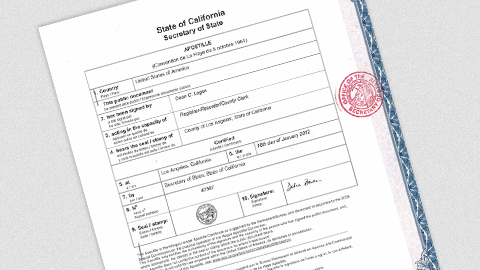
At its core, the apostille process involves the certification of public documents to verify their authenticity. This process is not merely about attaching a seal or stamp; it is a rigorous method of document ratification that confirms the validity of the document’s origin, the authority of the official who has signed it, and the identity of the seal or stamp it bears. Documents typically subjected to this process include diplomas, marriage certificates, birth certificates, legal contracts, and court orders.
The Legal Framework and International Implications
The legal framework of the apostille is grounded in international law, specifically tailored to facilitate the cross-border recognition of documents. It serves as a legal bridge between jurisdictions, ensuring that a document authenticated in one country is recognized as valid in another. This is particularly crucial in legal proceedings, educational credential verification, and international business transactions, where the authenticity of documents is paramount.
The Procedure: From Local to Global Recognition
Obtaining an apostille involves several key steps, starting with the verification of the document at the national level by a competent authority, such as a notary public or a government department. Once the national level authentication is complete, the document is then escalated to a higher authority, often a state department or foreign affairs ministry, which then affixes the apostille certificate. This certificate confirms that the document has been officially authenticated and is ready for international use.
Technological Advancements and the Apostille
With the advent of technology, the process of obtaining an apostille has evolved. Many jurisdictions now offer electronic apostilles, facilitating faster and more secure processing. This digital shift not only streamlines the process but also enhances the integrity and verification capabilities, ensuring that documents remain tamper-proof and their authenticity easily verifiable.
Navigating the Apostille for Various Document Types
The application of the apostille can vary depending on the type of document. For instance, educational documents such as diplomas require verification of academic credentials, while legal documents like power of attorney necessitate a thorough legal standing check. Each type of document undergoes a specific validation process to meet the apostille standards, ensuring that the document’s legal and official status is unquestionable.
Global Certification and Its Impact
The apostille’s role in global certification is monumental. It eliminates the cumbersome and often time-consuming process of document legalization across different countries, thereby facilitating smoother international interactions. Whether for personal or professional reasons, individuals and entities can leverage the apostille to authenticate their documents, ensuring global acceptance and recognition.
Conclusion: Apostille as a Keystone in International Documentation
The apostille emerges as a pivotal element in the sphere of international documentation, embodying the essence of legal authentication and international compliance. It stands as a testament to the cooperative efforts of countries to simplify and secure the process of document validation across borders. As the world continues to converge into a global village, the apostille remains a fundamental tool in bridging legal and bureaucratic divides, fostering trust, and facilitating international mobility and cooperation.